Smart City Technologies for Sustainable Growth
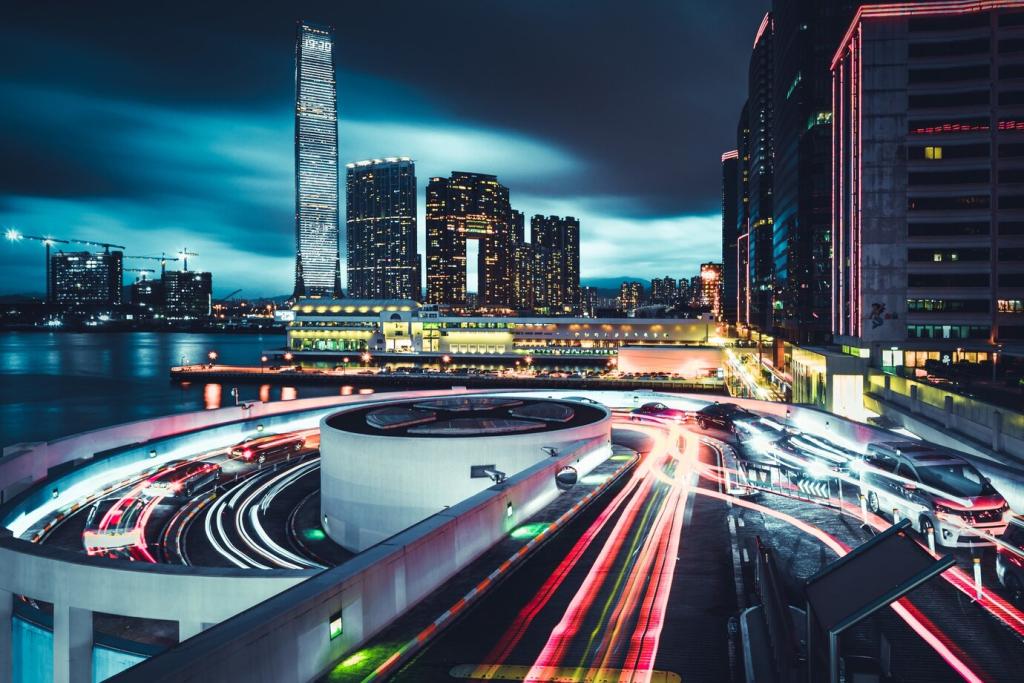
Smart city technologies are revolutionizing urban spaces by leveraging digital innovation to address growing sustainability concerns. These solutions span a wide array of applications, from optimizing energy usage to enhancing public services and facilitating citizen engagement. A sustainable smart city not only employs advanced technologies but also fosters economic development, environmental stewardship, and improved quality of life. This page explores the critical role that smart city technologies play in shaping resilient, efficient, and sustainable urban environments, ensuring that cities are equipped to meet future challenges and opportunities.
Digital Infrastructure for Urban Efficiency
Urban Connectivity Platforms
Urban connectivity platforms serve as the digital ecosystem that links various components of a city together, ensuring a seamless flow of information and collaboration among stakeholders. These platforms utilize IoT sensors, wireless communications, and cloud computing to collect and process vast amounts of urban data in real time. By interconnecting public services, utilities, and private enterprises, these platforms enable optimized resource allocation, improved emergency response, and predictive maintenance of city assets. The continuous evolution of urban connectivity platforms is critical to streamlining operations while minimizing waste and supporting environmentally conscious growth strategies.
Edge Computing in City Networks
Edge computing is reshaping the landscape of urban data management by processing information closer to its source rather than relying solely on distant data centers. Within smart cities, edge devices are deployed throughout public spaces, intersections, and infrastructure, allowing instant analysis and decision-making based on real-time conditions. This technology significantly reduces network latency, enhances privacy and security, and permits rapid responses to dynamic urban challenges, such as traffic congestion or air quality fluctuations. As cities strive for sustainability, edge computing ensures scalability, resilience, and energy efficiency across mission-critical applications.
5G Integration for Smart Solutions
The deployment of 5G networks in smart cities has unleashed a new era of high-speed, low-latency communications necessary for advanced urban technologies. With the capacity to simultaneously support millions of connected devices per square kilometer, 5G elevates the performance of smart traffic systems, autonomous vehicles, and interactive city services. Importantly, this enhanced connectivity underpins data-intensive applications that optimize energy consumption, support safety measures, and encourage active citizen engagement. As cities continue to expand, 5G integration stands as a pivotal enabler of long-term sustainability and innovation.
Green Mobility and Smart Transportation
Intelligent traffic management systems use sensors, cameras, and software platforms to monitor and optimize urban traffic flow. By proactively analyzing real-time data, these systems adjust traffic signals, reroute vehicles, and prioritize public transport to minimize congestion and reduce idle emissions. The result is smoother commutes, lower fuel consumption, and improved air quality. Moreover, intelligent traffic management facilitates the integration of new mobility solutions, including electric buses and bicycle-sharing programs, making transportation in smart cities more adaptive, sustainable, and accessible for all citizens.
The introduction of electric and autonomous vehicles (EVs and AVs) into urban landscapes represents a significant step forward in reducing a city’s carbon footprint and enhancing mobility equity. Charging infrastructure, remote monitoring, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication enable the seamless operation and scaling of these next-generation transportation solutions. With autonomous vehicles, smart routing algorithms can minimize travel time and energy use, while electric vehicles eliminate tailpipe emissions. Integrating EVs and AVs into the broader smart city network supports sustainable urban development goals and illustrates the transformative impact of technology on transportation.
Mobility-as-a-Service platforms are redefining transportation by unifying various mobility options into a single, user-centric experience. Powered by real-time data and digital payments, MaaS enables residents to plan, book, and pay for trips that combine public transit, bikes, rideshares, and more, all within a cohesive app. This approach not only encourages multimodal, greener travel choices but also streamlines mobility operations, improves cost efficiency, and reduces the need for private car ownership. Ultimately, MaaS platforms help cities decrease congestion, lower emissions, and advance toward a more sustainable urban future.
Urban Energy Optimization and Environmental Management
Smart Grids and Distributed Energy Resources
Smart grids combine traditional power infrastructure with digital communication and data analytics to improve efficiency, reliability, and flexibility in energy distribution. These networks support the integration of distributed energy resources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems, enabling cities to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Advanced sensors and intelligent controls help balance supply and demand in real time, optimize grid performance, and reduce waste. Through smart grids, urban areas can accommodate growing energy demands sustainably while enabling widespread adoption of clean energy solutions.
Building Automation and Energy Efficiency
The rise of building automation systems is revolutionizing how commercial and residential properties consume energy. IoT-enabled sensors and smart controls continuously monitor occupancy, lighting, heating, and cooling conditions, automatically adjusting settings to minimize waste and maximize comfort. These systems empower property managers and residents to track energy usage, implement efficiency upgrades, and participate in demand response programs. As a result, building automation is a cornerstone of urban sustainability efforts, sharply reducing energy consumption and lowering greenhouse gas emissions across the cityscape.
Environmental Monitoring and Pollution Control
Smart cities are leveraging advanced technologies to monitor air and water quality, track waste management operations, and predict environmental hazards. Deploying networks of connected sensors, cities gain access to real-time pollution data and can swiftly implement targeted interventions to protect public health. Technology-driven pollution control measures include automated street cleaning, smart waste collection, and predictive analytics to prevent contamination events. By continuously monitoring and managing environmental indicators, smart cities enhance resilience, improve livability, and accelerate progress toward ambitious sustainability goals.